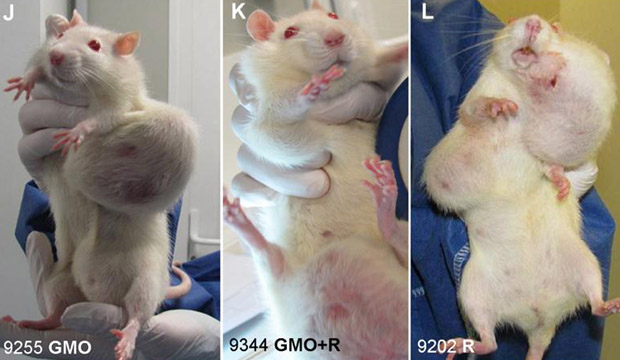
Source: es.landesbioscience.com
News article: sustainablepulse.com
Abstract
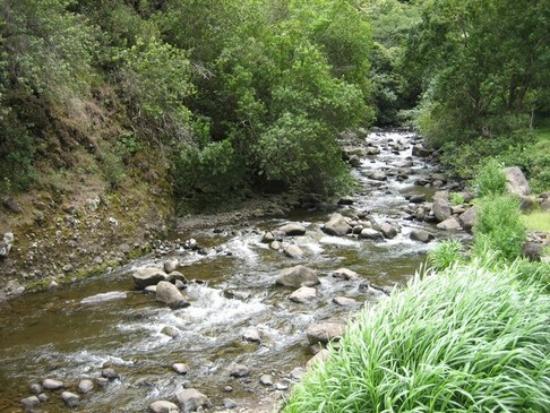
Multiple variants of the Cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter (P35S) are used to drive the expression of transgenes in genetically modified plants, for both research purposes and commercial applications. The genetic organization of the densely packed genome of this virus results in sequence overlap between P35S and viral gene VI, encoding the multifunctional P6 protein. The present paper investigates whether introduction of P35S variants by genetic transformation is likely to result in the expression of functional domains of the P6 protein and in potential impacts in transgenic plants. A bioinformatic analysis was performed to assess the safety for human and animal health of putative translation products of gene VI overlapping P35S. No relevant similarity was identified between the putative peptides and known allergens and toxins, using different databases. From a literature study it became clear that long variants of the P35S do contain an open reading frame, when expressed, might result in unintended phenotypic changes. A flowchart is proposed to evaluate possible unintended effects in plant transformants, based on the DNA sequence actually introduced and on the plant phenotype, taking into account the known effects of ectopically expressed P6 domains in model plants.
Authors
Nancy Podevin and Patrick du Jardin
Nancy Podevin Corresponding author: nancy.podevin@gmail.com
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Parma, Italy
Patrick du Jardin, Gembloux Agro-Bio Tech; Plant Biology Unit; University of Liège; Gembloux, Belgium