This study, published in the Journal of Environmental and Analytical Toxicology, reveals that industry studies on glyphosate dating back as far as the 1980s, including some by Monsanto, showed that the chemical caused birth defects in lab animals.
Source: Journal of Environmental and Analytical Toxicology
Abstract
The publication of a study in 2010, showing that a glyphosate herbicide formulation and glyphosate alone caused malformations in the embryos of Xenopus laevis and chickens through disruption of the retinoic acid signalling pathway, caused scientific and regulatory controversy. Debate centred on the effects of the production and consumption of genetically modified Roundup Ready® soy, which is engineered to tolerate applications of glyphosate herbicide. The study, along with others indicating teratogenic and reproductive effects from glyphosate herbicide exposure, was rebutted by the German Federal Office for Consumer Protection and Food Safety, BVL, as well as in industry-sponsored papers. These rebuttals relied partly on unpublished industry-sponsored studies commissioned for regulatory purposes, which, it was claimed, showed that glyphosate is not a teratogen or reproductive toxin.
However, examination of the German authorities’ draft assessment report on the industry studies, which underlies glyphosate’s EU authorisation, revealed further evidence of glyphosate’s teratogenicity. Many of the malformations found were of the type defined in the scientific literature as associated with retinoic acid teratogenesis. Nevertheless, the German and EU authorities minimized these findings in their assessment and set a potentially unsafe acceptable daily intake (ADI) level for glyphosate. This paper reviews the evidence on the teratogenicity and reproductive toxicity of glyphosate herbicides and concludes that a new and transparent risk assessment needs to be conducted. The new risk assessment must take into account all the data on the toxicity of glyphosate and its commercial formulations, including data generated by independent scientists and published in the peer-reviewed scientific literature, as well as the industry-sponsored studies.
Authors
M Antoniou, MEM Habib, CV Howard, RC Jennings, C Leifert, RO Nodari, CJ Robinson and J Fagan
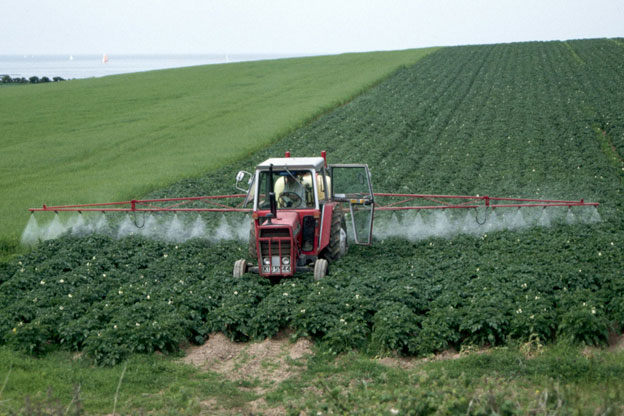


















































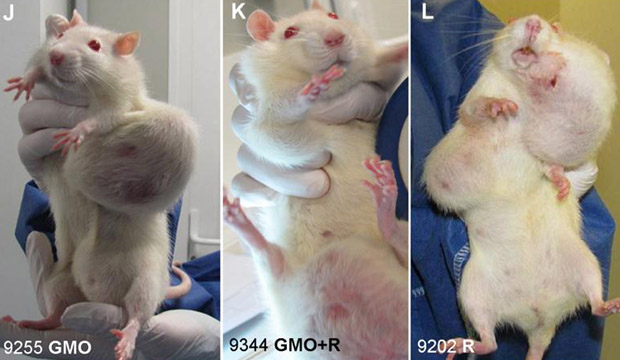










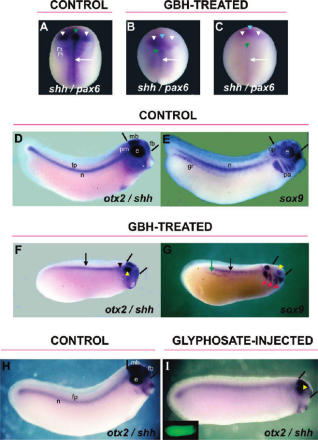







[…] The EU approval of glyphosate, the main ingredient of the herbicide Roundup, is based on bad science and a “don’t look, don’t see” attitude on the part of regulators, according to a new peer-reviewed study. […]
I am 63 years old. I moved to central IL in Nov 2009 to be csoelr to my aunt and cousins. I live in a small town surrounded by fields of roundup-ready corn and soybeans. Since spring of 2010 I have been almost incapacitated at times by shortness of breath, particularly when there is corn pollen in the air, and when the fields are disked or harvested. Considering that I moved from the LA basin, and before that lived next to the diesel-spewing largest rail shunt yard in the west, with NO breathing problems, this really puzzles me. I do have other pollen allergies, but they are the runny-nose type. My heart has been evaluated it works great. My lungs have been evaluated no COPD, no asthma, no obstruction, no tumors, no pneumonia they work fine. I am doing pulmonary rehab to see if it will help. One possibility is that irritation by pollen, particulates, etc. causes spasms of the bronchial tubes. I think it’s the GMO crops around me. I don’t have a large disposable income and I’d rather give the money to you than to the doctors, hospitals, labs, etc.